Switching power supply test requirements and procedures
Time:2022-09-16
Views:1772
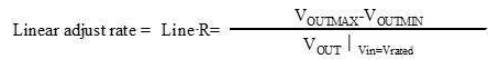
The voltage regulation test is called Line regulation test in English, which means the change rate of output voltage with input AC voltage when the power supply is under a certain load. It is investigated that when the input AC power grid voltage changes within a certain range, the output voltage of the power supply should not have too much jitter. It is generally set at ± 2% - ± 5%.

The test method is as follows
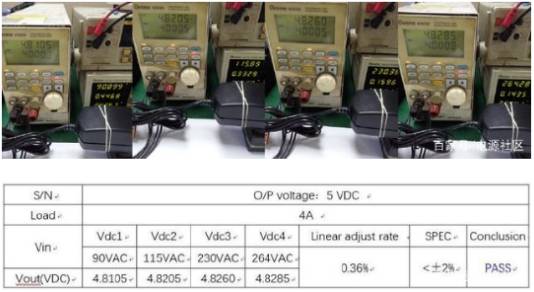
Measure the output change value when the input AC voltage changes from 90Vac to 264Vac under the calculation of a 5V4A adapter

Switching power supply test requirements and procedures
In the electronic environment, electromagnetic interference will have a certain impact on the work of the power supply. The power supply with small source effect and load effect has better stability, and electronic engineers should consider these aspects in the power supply design.
1、 Test items
The items to be measured include no-load output of switching power supply, voltage and current output under rated load, source effect, load effect, ripple, withstand voltage and insulation resistance, and short circuit protection (or overcurrent protection point).
The test shall refer to the detailed parameter specifications given by each switching power supply.
For more important power supply or power supply with power over tens of watts, its efficiency (or working temperature of internal power components) directly determines its reliability and failure rate, which shall be tested; In addition, there are many other indicators that should be tested according to different requirements, such as the instantaneous drop and recovery time of output voltage of sudden load, input power factor and waveform peak to peak ratio of AC/DC power supply, various EMC indicators of power supply, temperature coefficient, time stability, etc.
2、 Test requirements
2.1. The tester should be able to correctly use the digital multimeter, identify the pin diagram of the switching power supply, adjust the output voltage of the power supply, and have electrical knowledge.
2.2. It is required to use instruments with high accuracy and resolution as far as possible, and choose the instrument according to the actual situation.
2.3. Generally, the routine test is conducted under normal temperature and pressure. If there are special requirements for the test conditions, the test shall be conducted under the required conditions (for example, some need to simulate the working site environment, such as outdoor, rainy, sun exposure, etc.).
3、 Test method and process
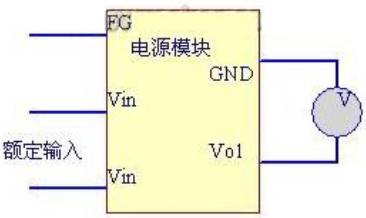
3.1 No load output voltage
3.1 No load output voltage
Adjust the input voltage of the switching power supply to the rated voltage of the switching power supply, and test the output voltage of the switching power supply with a multimeter. In order to reduce the error, several groups of data can be measured (the power switching power supply in the figure represents the detected switching power supply).

Figure 1 Schematic Diagram of No load Wiring
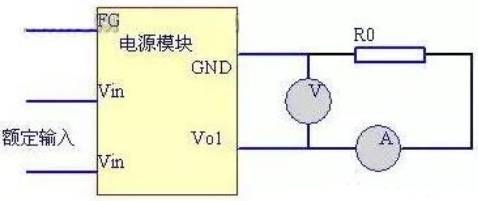
3.2 Switching power output under rated load
The test in this step includes the test of rated output voltage and current. First, determine the rated load of the switching power supply, and generally select the resistance as the load. Note that the power of the selected resistor must be far greater than the output power of the switching power supply to reduce the heating of the resistor. Some heat dissipation measures can also be added, such as placing an exhaust fan.
Calculation formula of rated load:
R0=U2/P
Note: where R0 is the rated load resistance value, U is the nominal output voltage value, and P is the rated power.
After determining the rated load, connect the rated input voltage of the switching power supply, connect the load circuit of the switching power supply, connect an ammeter in the load circuit (for safety meter, it is recommended to use a precision shunt resistor in series to measure its voltage drop and convert it to the current value), test the current in the circuit, and test the output voltage of the switching power supply with a multimeter voltage range. Record the voltage and current value. The wiring diagram is shown in Figure 2, where R0 is the rated load.

Fig. 2 Schematic Diagram of Rated Load Wiring
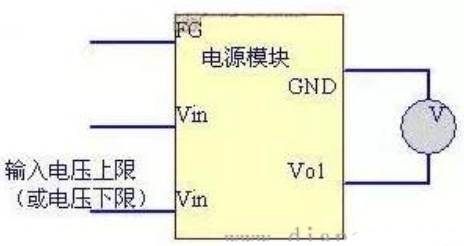
3.3 Source effect (i.e. voltage regulation)
Source effect refers to the change of output voltage relative to nominal output when the input voltage changes from low to high within the input voltage range of switching power supply.
Adjust the input voltage of the switching power supply to the lower limit and upper limit of the range, measure the output voltage of the switching power supply with a multimeter and record it.

Fig. 3 Source effect test
The calculation formula is: [(Vo1-Vo2)/Vo] * 100%
Note: Vo1 is the output voltage value measured at the input voltage, Vo2 is the output voltage value measured at the input voltage, and Vo is the nominal output voltage.
3.4 Load effect (i.e. current regulation rate)
Load effect refers to the change of switching power supply output voltage relative to the nominal value when the load changes from rated load to half load (or 20% load) under rated voltage.
The important task of this step is to determine the load. The percentage of load is calculated according to the current, that is, the percentage of half load (or 20% load) current to the rated current. According to the calculated current value, the resistance value can be inferred for selection.
Load calculation formula under half load:
R1=(U2/P)*2
Note: R1 is the load resistance under half load, that is, twice the rated load.
R1 in the figure is the inferred equivalent load.

Figure 4 Load Effect Test
The calculation formula is: [(Vo ‘- V amount)/Vo] * 100%
Note: Vo ‘is the output voltage of the switching power supply measured after the percentage equivalent resistance is connected to the switching power supply output circuit. The V rating is the output voltage of the switching power supply measured under the rated load, and Vo is the nominal output voltage.

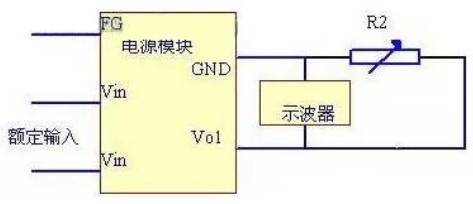
3.5 Ripple
Under the condition of rated input voltage when the switching power supply is unloaded to full load, multipoint or continuously and evenly changing (generally testing the ripple under no-load, half load and full load), adjust the oscilloscope to 20MHZ, AC coupling mode, appropriate scanning cycle, clamp the grounding clamp of the oscilloscope to the GND end of the switching power supply output, contact the Vo end of the switching power supply output with a stylus, and read the peak and peak values of the ripple in the oscilloscope.
Fig. 5 Ripple test
For AC/DC power supply, it shall be observed when the oscilloscope scanning speed can display several AC cycles under full load. The "bandwidth attenuation" of the oscilloscope shall be set to the off (non attenuation) state.
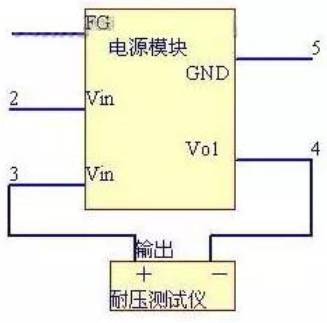
3.6 Withstand voltage and insulation resistance
The withstand voltage is tested with a withstand voltage tester. According to the technical data provided by the switching power supply, find out the reference value of withstand voltage, turn on the power supply of the withstand voltage tester, and set parameters, including AC/DC, range, leakage current and time settings. After setting, start the withstand voltage tester to observe the over leakage alarm. If the over leakage alarm occurs, the leakage current should be small, and the leakage current should be increased or the test voltage should be reduced. The withstand voltage between 1, 4 and 1, 2, 3 and 4 shall be tested respectively.
Fig. 6 Voltage withstand test
The insulation resistance shall be tested with a megger. Clamp the two ends of the megger with appropriate working voltage to the two ends to be tested, quickly shake the handle until the clutch slips, read the value, or use an electronic megger for testing.
3.7 Short circuit protection characteristics (or overcurrent protection point)
This depends on the description given in the technical data. For example, the description of switching power supply is: the short circuit protection feature is long-term self recovery, which can be tested by connecting a wire to the output terminal of the switching power supply, and observed for a long time (as required). The voltage output during the short circuit and the switching power supply output after the short circuit is eliminated.

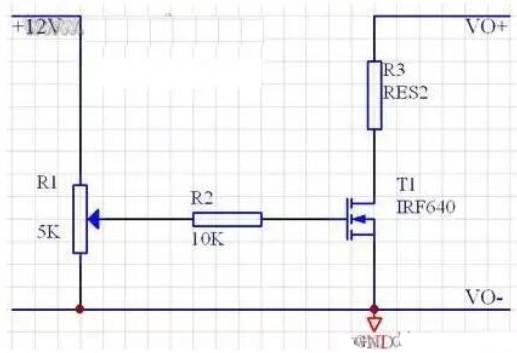
Fig. 7 Reference circuit for overcurrent protection point test
R3 in the figure represents a current that can produce twice the rated load (that is, the resistance of R3 is half of the rated load at this time). VO+and VO - are respectively connected to the positive and negative output terminals of the switching power supply.
The meaning of over-current protection point is that when the current in the circuit reaches a certain value, the switching power supply will cut off the output (Note: Note that the over-current protection of some switching power supplies is not cut off but may be current limiting). A variable load is connected in series in the output circuit of the switching power supply (the variable range is required to be large enough), and the current in the circuit is adjusted by adjusting the variable load. During the current rise, pay attention to the reading of the ammeter, and read the value before the current changes to 0 (or a very small or small value), It is the over-current protection point of the switching power supply (pay attention to the heat dissipation of the resistance at this time, because the resistance heats more than the rated output under the over-current condition).
4、 Test record and data processing
The data and abnormal conditions shall be recorded in detail for each test step. If there are abnormal conditions, the causes shall be analyzed. The data shall be recorded for the evaluation of calculation parameters and switching power supply.
Data processing:
1. Average value processing
2. Source effect calculation
The formula is:
[(Vo1-Vo2)/Vo]*100%
Note: Vo1 is the output voltage value measured at the input voltage, Vo2 is the output voltage value measured at the input voltage, and Vo is the nominal output voltage.
3. Calculation of load effect
The formula is:
[(Vo ‘- V amount)/Vo] * 100%
Note: Vo ‘is the output voltage of the switching power supply measured after the percentage equivalent resistance is connected to the switching power supply output circuit. The V rating is the output voltage of the switching power supply measured under the rated load, and Vo is the nominal output voltage. In addition, electronic engineers can pay more attention to the electronic exhibition and understand the product technology in the industry, which is good for them.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |